Basic Concepts
Microwave Theoretical Consideration
What are Microwaves?
Definition
- Electromagnetic wave in frequency of 300MHz ~ 300GHz
Industrial Frequency and Features
- Frequency : 433MHz, 915MHz, 2.45GHz
- 433MHz, 915MHz : industrial applied drying field
- 2.45GHz : ceramic drying / sintering, chemical reaction, organic compound Curing, food heat treatment/sterilization
- Others : application of 28GHz, 60GHz depending on purpose
Principal of Dielectric Heat
Principal of Dielectric Heat
Adding electric field to a dielectric substance with a pair of +ion and –electron arranges the pair along the electric field. If added backward, the array reverses as well. Inner heating by dipole revolution or vibration within molecules.
Heat Convert Power Loss P
Power loss(P) that becomes heat within a dielectric substance
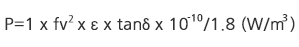
(Note) f:Hz, v: size of electric field, ε: specific inductive capacity, tanδ:loss factor


